identifying grapth flattening
Grapth flattening is a means of obscuring the flow of execution to prevent static review of reverse engineered code. Lets take a look at how to identify when control grapth flattening is being used.
Start by loading the sample emotet in miasm.
import sys
import subprocess
import graphviz
# import z3
import IPython
from miasm.analysis.binary import Container
from miasm.analysis.machine import Machine
from miasm.core.locationdb import LocationDB# initsymbol table
loc_db=LocationDB()
# as we explore, we can name more memory locations
loc_db.add_location(offset=0x405c49, name="return_zero")
loc_db.add_location(offset=0x4063f0, name="flat_function")fname="/home/user/Desktop/samples/emotet"
# read binary file
container=Container.from_stream(open(fname,'rb'), loc_db)
# getCPU abstraction
machine=Machine(container.arch)
# disassembly engine
mdis=machine.dis_engine(container.bin_stream, loc_db=loc_db)The magic number of a binrary tells us what kind of file it is. This is an executable PE.
If we add the Entrypoint offset to the ImageBase address we know whereabouts the sample starts.
We can get all of this information from 'readpe'.
# readpe -H emotet
result=subprocess.run(["readpe", "-H", fname])
result DOS Header
Magic number: 0x5a4d (MZ)
Bytes in last page: 144
Pages in file: 3
Relocations: 0
Size of header in paragraphs: 4
Minimum extra paragraphs: 0
Maximum extra paragraphs: 65535
Initial (relative) SS value: 0
Initial SP value: 0xb8
Initial IP value: 0
Initial (relative) CS value: 0
Address of relocation table: 0x40
Overlay number: 0
OEM identifier: 0
OEM information: 0
PE header offset: 0xc0
COFF/File header
Machine: 0x14c IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_I386
Number of sections: 4
Date/time stamp: 1599761546 (Thu, 10 Sep 2020 18:12:26 UTC)
Symbol Table offset: 0
Number of symbols: 0
Size of optional header: 0xe0
Characteristi
cs: 0x102
Characteristics names
IMAGE_FILE_EXECUTABLE_IMAGE
IMAGE_FILE_32BIT_MACHINE
Optional/Image header
Magic number: 0x10b (PE32)
Linker major version: 12
Linker minor version: 0
Size of .text section: 0xa600
Size of .data section: 0x1c00
Size of .bss section: 0
Entrypoint: 0x5c20
Address of .text section: 0x1000
Address of .data section: 0xc000
ImageBase: 0x400000
Alignment of sections: 0x1000
Alignment factor: 0x200
Major version of required OS: 6
Minor version of required OS: 0
Major version of image: 0
Minor version of image: 0
Major version of subsystem: 6
Minor version of subsystem: 0
Size of image: 0x10000
Size of headers: 0x400
Checksum: 0
Subsystem required: 0x2 (IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_GUI)
DLL characteristics: 0x8740
DLL characteristics names
IMAGE_DLLCHARACTERISTICS_DYNAMIC_BASE
IMAGE_DLLCHARACTERISTICS_NX_COMPAT
IMAGE_DLLCHARACTERISTICS_NO_ISOLATION
IMAGE_DLLCHARACTERISTICS_NO_SEH
IMAGE_DLLCHARACTERISTICS_TERMINAL_SERVER_AWARE
Size of stack to reserve: 0x100000
Size of stack to commit: 0x1000
Size of heap space to reserve: 0x100000
Size of heap space to commit: 0x1000
We can start exploring the control flow grapth at this calculated address.
'''
Entrypoint: 0x5c20
ImageBase: 0x400000
'''
entry_point=0x00405c20
# retriev eall basic blocks starting at entry point
asm_cfg=mdis.dis_multiblock(entry_point)
# display CFG
dot = asm_cfg.dot()
gvz=graphviz.Source(dot)
display(gvz)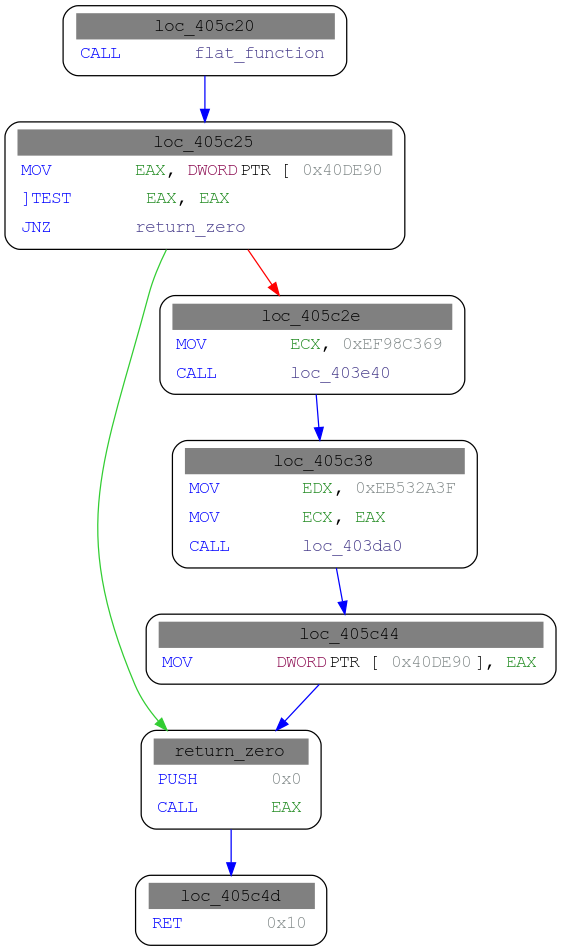
Start with looking at calls and long jumps.
offset=0x4063f0
# retrieve all basic blocks starting at entry point
asm_cfg=mdis.dis_multiblock(offset)
# display CFG
dot = asm_cfg.dot()
gvz=graphviz.Source(dot)
# weird error will not display?
# save to file, convert to png
gvz.save("./flat_grapth.dot")
result=subprocess.run(["dot", "-Tsvg", "flat_grapth.dot", "-o", "flat_graph.svg"])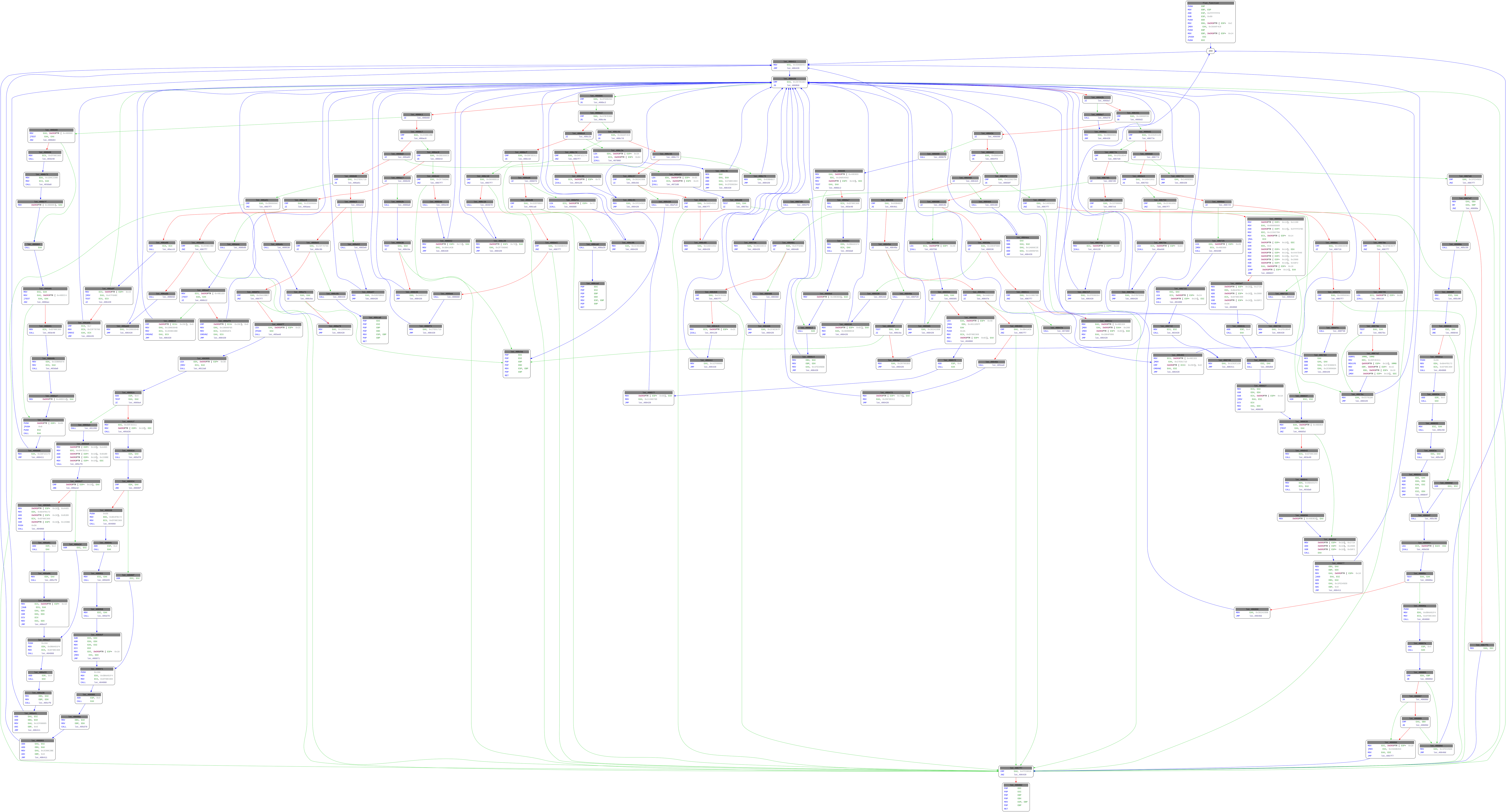
This CFG is "flattened" and highly complex. Which block runs is determined by a state variable-- a value in EAX.
We can determine the order of basic blocks by just running the code, or build some kind of solver to trace it statically, which we can discuss in the later posts.
sources
https://www.williballenthin.com/post/2020-01-12-miasm-part-2/
https://infosecadalid.com/2021/08/27/my-introduction-to-z3-and-solving-satisfiability-problems/
https://github.com/mrphrazer/obfuscation_detection/tree/main/examples
- ← Previous
simple analysis - Next →
visual binary